Breaking News


Popular News

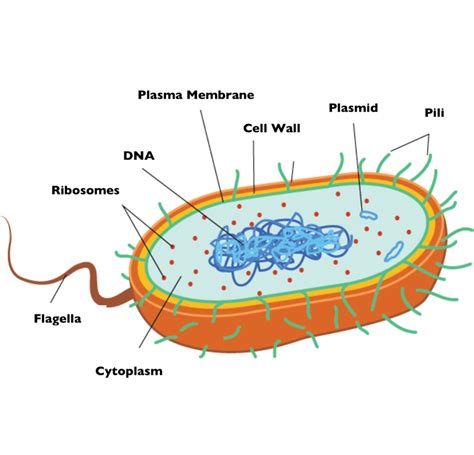
Explore the fundamental concepts of biology including cells, DNA, and microorganisms. Learn about cell structure, DNA function, and the relationship between DNA and traits.When it comes to understanding the fundamental principles of biology, it all starts with the building blocks of life – cells, DNA, and microorganisms. These concepts form the foundation of how living organisms function and interact with their environment. In this blog post, we’ll explore the basics of biology, starting with an in-depth look at what cells are and how they function. We’ll then delve into the intricate structure of DNA and the crucial role it plays in determining an organism’s traits. Additionally, we’ll discuss the various types of microorganisms that exist and their impact on the world around us. By the end of this post, you’ll have a foundational understanding of these key biological components and their interconnectedness, setting the stage for more advanced topics in the field of biology. Join us on this journey as we unravel the complexities of life at its most fundamental level.
Contents

Cells are the basic building blocks of all living organisms. They are the smallest unit of life and are often referred to as the building blocks of life. Each cell is enclosed by a membrane that separates the interior of the cell from the external environment. Within the cell, there are various organelles that perform specific functions necessary for the cell’s survival and replication.
Cells can be grouped into two broad categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, do not have a true nucleus, while eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, and fungi, have a distinct nucleus that houses the genetic material. In addition to genetic material, cells also contain ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis, and mitochondria, the powerhouse of the cell that generates energy.
These complex, yet tiny units are the foundation of life, playing a crucial role in growth, development, and reproduction. Understanding the structure and function of cells is essential not only in biology but also in fields such as medicine and biotechnology. They form the basis of life, and without them, the existence of living organisms as we know it would not be possible.
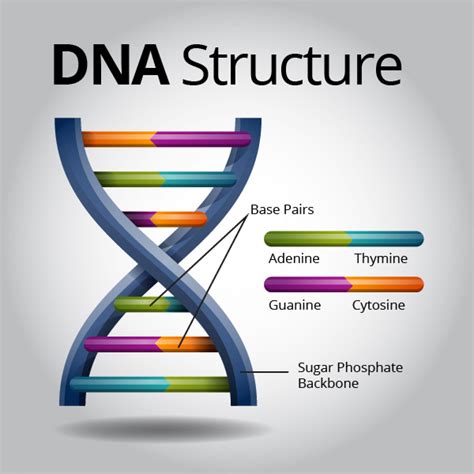
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. It is often referred to as the “building blocks of life” due to its crucial role in determining an organism’s traits and characteristics. The structure of DNA is composed of two strands that coil around each other to form a double helix, which resembles a twisted ladder. Each strand contains a sequence of four different nucleotides – adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These nucleotides are paired together in a specific way, with adenine always pairing with thymine, and cytosine always pairing with guanine.
In addition to the base pairs, the structure of DNA also includes sugar and phosphate molecules, which form the backbone of the molecule. The arrangement of these components creates a stable and durable molecule that is capable of storing and transmitting genetic information. The structure of DNA can be visualized as a ladder, with the base pairs forming the rungs, and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the sides. This elegant and efficient design allows DNA to carry the instructions necessary for the production of proteins, which are essential for the growth and maintenance of an organism.
The structure of DNA is not only important for storing and transmitting genetic information, but it also plays a critical role in the process of replication. When a cell divides, the DNA must be accurately copied to ensure that each new cell receives a complete set of genetic instructions. The double helix structure of DNA allows the molecule to unwind and separate, enabling each strand to serve as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. This process of DNA replication is essential for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine | Form base pairs and determine genetic code |
| Sugar and phosphate molecules | Form the backbone of the DNA molecule |
| Double helix structure | Allows for stable storage and replication of genetic information |
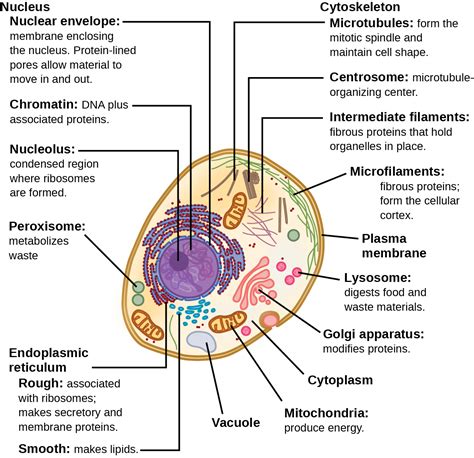
Organelles are specialized structures within a cell that have specific functions, helping the cell carry out essential tasks for survival. Each organelle performs a specific function, contributing to the overall health and function of the cell. Understanding the functions of organelles is crucial in comprehending the complex processes that occur within cells.
One of the most important organelles within a cell is the nucleus, often referred to as the control center of the cell. The nucleus contains the cell’s genetic material, including DNA, and is responsible for regulating gene expression and controlling the cell’s activities. It plays a vital role in cellular reproduction and determining the cell’s characteristics.
Another essential organelle is the mitochondria, often described as the powerhouse of the cell. Mitochondria are responsible for generating energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through a process called cellular respiration. This energy is essential for the cell’s metabolic activities and overall function. Without mitochondria, the cell would not be able to produce the energy necessary for survival.
Additionally, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an organelle involved in the synthesis, folding, and transport of proteins within the cell. There are two types of ER: rough ER, which has ribosomes attached to its surface and is involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which plays a role in lipid synthesis and detoxification. The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi complex, works in conjunction with the ER to modify, sort, and package proteins for secretion or delivery to other organelles within the cell.
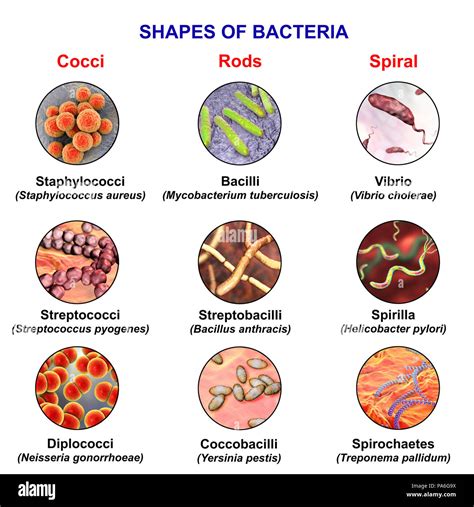
Microorganisms are tiny, living organisms that are too small to see without a microscope. They are incredibly diverse, and are found in almost every environment on Earth. Some of the main types of microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa.
Bacteria are single-celled organisms that can be found in various environments such as soil, water, and even in the human body. They come in different shapes and sizes, and can either be beneficial or harmful to humans. Some bacteria play a crucial role in processes like fermentation, while others can cause diseases such as strep throat and tuberculosis.
Viruses, on the other hand, are much smaller than bacteria and are not considered living organisms. They can only reproduce inside the cells of other organisms, and are known for causing illnesses such as the flu, common cold, and COVID-19.
Fungi are a group of organisms that include yeasts, molds, and mushrooms. They can be found in various habitats, and play important roles in the ecosystem by breaking down organic matter. Some fungi can cause infections in humans, while others are used to produce antibiotics and food products like bread and cheese.
Lastly, protozoa are single-celled organisms that are found in water and soil. They come in different shapes and sizes, and are an essential part of the food chain, as they serve as food for other microorganisms. Some protozoa can also cause diseases such as malaria and dysentery.
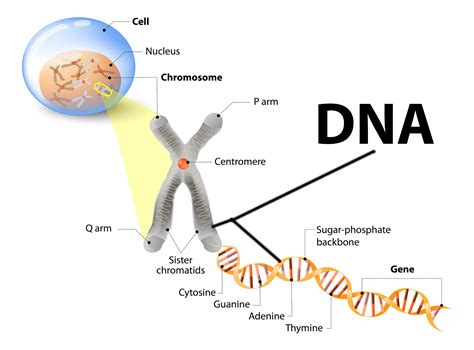
Relationship between DNA and traits
When it comes to understanding the relationship between DNA and traits, it’s important to recognize that DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic material that carries the instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known organisms. This complex molecule consists of two strands that coil around each other to form a double helix, with each strand made up of a series of nucleotides. These nucleotides contain the genetic code that determines an individual’s inherited traits.
DNA contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism, and these instructions are carried out by the process of gene expression. Genes are specific sequences of DNA that code for particular proteins, which in turn determine various traits such as eye color, hair texture, and susceptibility to certain diseases. However, it’s important to note that while DNA provides the blueprint for an organism’s traits, the environment and other factors also play a role in determining how these traits are expressed.
Understanding the relationship between DNA and traits is crucial in fields such as genetics, medicine, and evolutionary biology. Researchers and scientists continue to study and unravel the complexities of DNA and its impact on traits in order to gain insights into human health, genetic disorders, and evolution. By gaining a deeper understanding of how DNA influences traits, we can potentially develop targeted treatments for genetic diseases and gain a better understanding of the diversity of life on Earth.
| Key Concepts | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Gene Expression | The process by which the information encoded in a gene is used to direct the assembly of a protein molecule. |
| Inherited Traits | Characteristics that are passed from parents to offspring through their genes. |
| Environment | External factors that can influence how traits are expressed, in addition to genetic factors. |

What is a cell?
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently.
What is DNA?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that carries the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses.
How do cells function?
Cells carry out functions necessary for life, such as obtaining nutrients, converting those nutrients into energy, and carrying out specialized functions. They also reproduce to create new cells.
What are microorganisms?
Microorganisms are organisms that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and some parasites, and they play important roles in various ecological and environmental processes.
How do cells and DNA relate to each other?
DNA is found in a cell’s nucleus and contains the instructions for making proteins, which carry out the functions of a cell. The DNA in a cell ultimately determines the cell’s structure and function.
What are the different types of cells?
There are two main types of cells: prokaryotic cells, which are simpler and do not have a true nucleus, and eukaryotic cells, which have a defined nucleus and other organelles.
How do microorganisms impact the environment?
Microorganisms play crucial roles in nutrient recycling, decomposition, and symbiotic relationships with other organisms. They also have both positive and negative effects on human health and the economy.