Breaking News


Popular News


Discover the rise of decentralized finance and its impact on traditional banking, the advantages and challenges, regulatory implications, and the future of DeFi.Decentralized finance, or DeFi, is revolutionizing the way we think about and interact with traditional banking systems. In recent years, the emergence of DeFi has presented a new, decentralized approach to financial services, offering individuals the opportunity to access a wide range of financial products and services without the need for traditional intermediaries. In this blog post, we will explore the rise of DeFi, its impact on traditional banking, and the regulatory implications it poses. We will also discuss the challenges faced by traditional banking institutions in the face of this disruptive technology, as well as the advantages and future potential of decentralized finance. Join us as we delve into the world of DeFi and its potential to reshape the financial landscape as we know it.
Contents

Decentralized finance (DeFi) refers to the movement that aims to create an open-source, permissionless, and transparent financial service ecosystem that is available to everyone and operates without any central authority or intermediaries. In traditional finance, banks and financial institutions act as intermediaries, facilitating transactions and providing various financial services. However, DeFi seeks to eliminate the need for these intermediaries by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to create decentralized applications (dApps) that can provide a wide range of financial services, including lending, borrowing, trading, and investment.
One of the key principles of DeFi is the concept of decentralization, which means that no single entity has control over the network, and all transactions and agreements are executed in a transparent and trustless manner. This not only reduces the risk of censorship and fraud but also allows for greater financial inclusion and access to services for individuals who are underserved or unbanked.
Some of the most popular DeFi protocols and platforms include Uniswap, Compound, MakerDAO, and Aave, each offering unique financial services and opportunities for users to interact with the ecosystem. These protocols are governed by community consensus and rely on open-source code, enabling anyone to participate in the network and contribute to its development.
In summary, decentralized finance represents a paradigm shift in the way financial services are accessed and operated, providing a more inclusive, transparent, and efficient alternative to traditional banking and finance.

The Rise of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized Finance, commonly referred to as DeFi, has emerged as a disruptive force in the traditional banking sector. Unlike traditional finance, which is centralized and relies on intermediaries such as banks and financial institutions, DeFi operates on a decentralized network using blockchain technology. This allows for peer-to-peer transactions, eliminating the need for intermediaries and providing greater financial inclusivity.
One of the key features of DeFi is its accessibility. Anyone with an internet connection and a smartphone or computer can access DeFi services, making it particularly appealing to those who are underserved or excluded from the traditional banking system. This accessibility has contributed to the rapid rise of DeFi, as it has the potential to reach a global audience and provide financial services to individuals who were previously unable to access them.
Furthermore, the rise of DeFi has been fueled by the growing demand for financial innovation and alternative investment opportunities. With DeFi, users can participate in a wide range of financial activities, including lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest on their digital assets. This has opened up new avenues for individuals to manage and grow their wealth outside of the traditional banking system.
As DeFi continues to gain momentum, it has the potential to revolutionize the traditional banking sector and reshape the way financial services are accessed and utilized. Its disruptive nature poses a challenge to traditional banking as it offers a more efficient, transparent, and accessible alternative to the current centralized system.
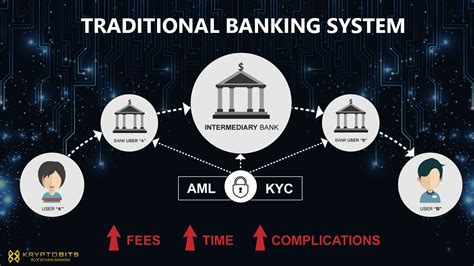
Traditional banking institutions face several challenges in today’s rapidly evolving financial landscape. One major challenge is the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) which has disrupted the traditional banking model. DeFi offers an alternative to traditional banking services by leveraging blockchain technology to provide financial products and services without the need for intermediaries.
Another challenge for traditional banks is the increasing competition from digital banks and fintech companies. These new entrants are able to offer more agile and cost-effective solutions, as they have the advantage of not being burdened by legacy systems and infrastructure. This puts traditional banks at a disadvantage in terms of innovating and keeping up with customer demands.
Furthermore, traditional banks are faced with the challenge of maintaining customer trust and confidence in the wake of various data breaches and cybersecurity threats. Customers are becoming increasingly concerned about the security of their personal and financial information, and any breach in security can have damaging consequences for a bank’s reputation and customer loyalty.
Lastly, traditional banks are struggling to adapt to the changing regulatory landscape, which has become more complex and stringent in response to evolving financial technologies. Compliance with regulatory requirements has become increasingly costly and time-consuming, putting additional strain on traditional banking institutions.
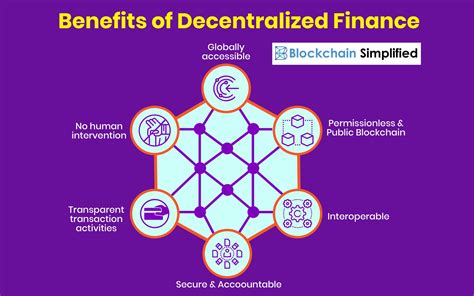
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is rapidly transforming the way traditional banking operates. The integration of blockchain technology has brought about a system that enables direct peer-to-peer transactions, cutting out the need for intermediaries such as banks. This disruption has a significant impact on the traditional banking sector, challenging its monopoly over financial services.
The emergence of DeFi has brought several advantages over traditional banking. With the use of smart contracts, decentralized lending and borrowing platforms have been established, providing individuals and businesses with access to financial services without relying on banks. This has expanded financial inclusion by offering opportunities to those who were previously excluded from the traditional banking system.
Furthermore, the transparency and security of blockchain technology have made financial transactions more secure and efficient. The immutability of distributed ledgers ensures that records cannot be altered, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust in financial transactions. As a result, the trust in traditional banking systems has been shaken, as customers seek more secure and convenient alternatives provided by DeFi platforms.
As DeFi continues to gain momentum, traditional banks are facing the challenge of adapting to this new decentralized system. The rise of decentralized finance threatens the traditional banking business model, forcing banks to reconsider their strategies and services to remain competitive in the evolving financial landscape.
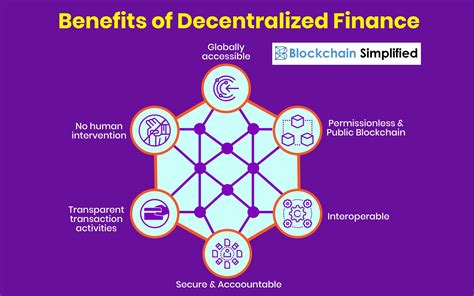
Advantages of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a rapidly growing sector that is poised to disrupt the traditional banking industry. One of the key advantages of DeFi is the potential for greater financial inclusion. By leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi has the ability to provide financial services to individuals who are underserved or excluded by the current banking system. This includes individuals in developing countries, as well as those who may not have access to traditional banking services due to a lack of credit history or identification. By removing the need for intermediaries, DeFi can also reduce the cost of financial services, making them more accessible to a wider range of people.
Another advantage of DeFi is the potential for increased transparency and security. With traditional banking, there is often a lack of transparency around fees, interest rates, and other terms and conditions. This can lead to confusion and mistrust among consumers. In contrast, DeFi applications are often built on open, public blockchains, which provide a high degree of transparency. Smart contracts, an essential component of DeFi applications, also ensure that agreements are automatically enforced without the need for intermediaries. This can reduce the risk of fraud and provide users with greater confidence in the security of their financial transactions.
Furthermore, DeFi offers the potential for greater innovation and flexibility in the development of financial products and services. Traditional banks are often hindered by legacy systems and slow to adopt new technologies. In contrast, DeFi is built on a foundation of blockchain technology, which allows for faster and more efficient innovation. This has led to the creation of a wide range of decentralized applications, including lending platforms, decentralized exchanges, and asset management tools. These applications offer users greater flexibility and choice, allowing them to customize their financial experience to better meet their individual needs.
In addition, DeFi has the potential to offer greater resilience and stability in the face of economic uncertainty. Traditional banks are often vulnerable to economic downturns and geopolitical instability, which can impact the stability of the financial system as a whole. DeFi, on the other hand, is built on decentralized networks that are less prone to single points of failure. This can provide users with greater confidence that their financial assets will remain secure and accessible, even during times of crisis.
In recent years, the emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi) has posed significant challenges to traditional banking institutions, prompting regulators to reevaluate their approach to financial oversight and compliance. The decentralized nature of DeFi, facilitated by blockchain technology, has introduced a new paradigm that operates outside of the traditional regulatory framework.
One of the key regulatory implications of DeFi is the difficulty in enforcing traditional financial laws and regulations on decentralized platforms. These platforms often operate across multiple jurisdictions and are governed by smart contracts, making it challenging for regulators to monitor and enforce compliance. This presents a potential loophole for illicit activities such as money laundering and terrorism financing.
Furthermore, the lack of intermediaries in DeFi raises concerns about consumer protection and financial stability. Without centralized institutions to oversee transactions and provide recourse for disputes, consumers may be vulnerable to fraud and other risks. Additionally, the interconnectedness of DeFi protocols could pose systemic risks to the broader financial system, requiring regulators to develop new approaches to mitigate these risks.
While DeFi holds great potential for financial inclusion and innovation, regulators are grappling with the need to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring financial stability and consumer protection. As the DeFi ecosystem continues to evolve, regulators face the challenge of adapting existing regulatory frameworks to effectively govern decentralized financial activities while fostering innovation and competitiveness.

Future of Decentralized Finance
Decentralized Finance, also known as DeFi, has been making waves in the world of finance in recent years. The concept of DeFi revolves around the idea of creating a financial system that operates without central authorities such as banks or governments. Instead, transactions are facilitated through smart contracts on blockchain networks, allowing for greater transparency and accessibility.
One of the key advantages of DeFi is its ability to provide financial services to those who are underserved or unbanked. By leveraging blockchain technology, DeFi platforms have the potential to reach individuals who may not have access to traditional banking services. This could have a profound impact on the global economy, as it opens up new opportunities for financial inclusion and innovation.
As with any emerging technology, DeFi also faces its fair share of challenges. Security risks, regulatory uncertainty, and scalability issues are just a few of the hurdles that the DeFi ecosystem must overcome in order to achieve widespread adoption. However, the potential benefits of DeFi are too great to ignore, and many experts believe that it has the potential to revolutionize the financial industry in the coming years.
| Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|
|
|
The future of decentralized finance looks promising, as more and more investors and institutions become aware of its potential. With the rise of decentralized applications and the growing popularity of cryptocurrencies, the DeFi ecosystem is poised for significant growth in the coming years. In fact, some analysts predict that the total value locked in DeFi protocols could surpass $1 trillion in the near future, signaling a major shift in the way that financial services are accessed and utilized.

What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to financial services that are built on blockchain technology, allowing for peer-to-peer transactions without the need for traditional intermediaries such as banks.
How does DeFi disrupt traditional banking?
DeFi disrupts traditional banking by offering more accessible, transparent, and efficient financial services, enabling individuals to have more control over their assets and access to a wider range of financial products and services.
What are the benefits of Decentralized Finance?
The benefits of Decentralized Finance include lower barriers to entry, increased financial inclusion, reduced transaction costs, greater financial transparency, and the potential for global access to financial services.
Are there any risks associated with DeFi?
Yes, there are risks associated with DeFi such as smart contract vulnerabilities, regulatory uncertainty, and potential security breaches on decentralized platforms.
What are some popular DeFi platforms?
Some popular DeFi platforms include Uniswap, Compound, Aave, MakerDAO, and SushiSwap, among others.
How can individuals participate in DeFi?
Individuals can participate in DeFi by using decentralized applications (DApps) to access lending, borrowing, trading, and other financial services, as well as by providing liquidity to decentralized exchanges.
Is DeFi the future of finance?
While DeFi shows great potential to transform the financial industry, its future is still uncertain and dependent on regulatory developments, technological advancements, and user adoption.