Breaking News


Popular News

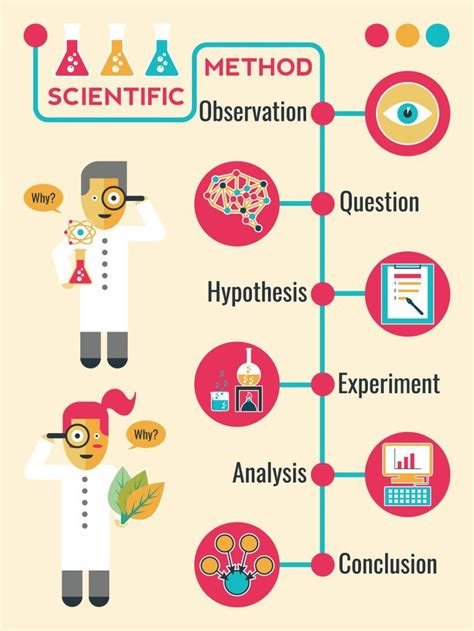
Learn the step-by-step guide to the scientific method, from making observations to analyzing data. Follow a systematic approach to understanding the scientific process.Are you curious about how scientists discover new knowledge and test their ideas? The scientific method is a systematic approach that scientists use to investigate and understand the world around us. In this blog post, we will explore the key steps of the scientific method and its importance in research and discovery.
From making observations to formulating hypotheses, designing experiments, and collecting data, each step in the scientific method plays a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of the natural world. By following a systematic approach, scientists can ensure that their findings are reliable and credible, ultimately advancing our understanding of the universe.
Join us as we delve into the step-by-step process of the scientific method, and gain a deeper understanding of the essential principles that underpin scientific inquiry. Whether you are a student, a researcher, or simply an inquisitive mind, this blog post will provide valuable insights into how science is conducted and how new knowledge is generated. Let’s embark on a journey of discovery together!
Contents
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand natural phenomena. It serves as a guide for conducting research and experiments in various fields of study, such as biology, chemistry, physics, and environmental science. By following this method, scientists can gather reliable and unbiased information, make logical interpretations, and draw well-supported conclusions.
One of the key principles of the scientific method is the requirement for evidence-based reasoning. This means that scientific claims and theories must be supported by empirical evidence obtained through systematic observation and experimentation. By using this approach, scientists can effectively test hypotheses, identify patterns, and uncover new knowledge about the world around us.
Another important aspect of the scientific method is its emphasis on objectivity and reproducibility. In order to ensure the reliability of their findings, scientists strive to eliminate bias and minimize errors in their experiments. They also aim to provide enough detail and clarity in their methods so that other researchers can replicate their work and verify the results. This commitment to transparency and consistency is crucial for building a solid foundation of scientific knowledge.
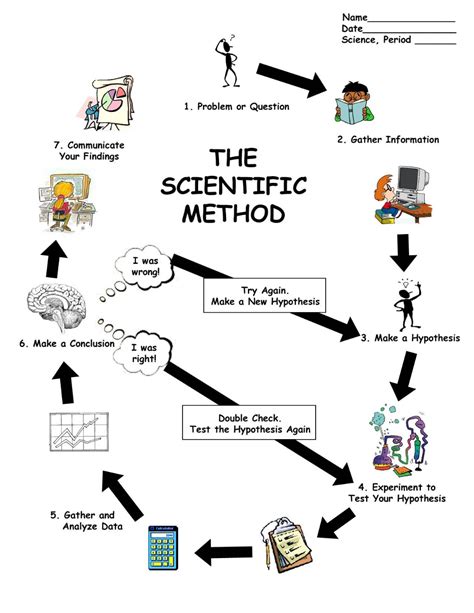
Overall, the scientific method is a powerful tool that enables scientists to approach problems in a systematic and organized manner. It provides a framework for generating testable hypotheses, conducting rigorous experiments, and drawing well-supported conclusions. By understanding the principles and steps of the scientific method, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the process of scientific inquiry and the value of evidence-based reasoning.
When it comes to conducting scientific research, it is of utmost importance to follow a systematic approach. This is because a systematic approach ensures that the entire process is organized and structured, which ultimately leads to reliable and credible results. Without a systematic approach, there is a risk of overlooking important details, leading to flawed conclusions and inaccurate findings.
Following a systematic approach also allows for reproducibility of results, which is a fundamental aspect of the scientific method. By clearly outlining each step in the research process, other scientists are able to replicate the study and verify the findings. This builds trust within the scientific community and contributes to the overall advancement of knowledge in the field.
Furthermore, a systematic approach provides a clear framework for researchers to follow, ensuring that no crucial steps are skipped or neglected. This is especially important in complex research projects where multiple variables and factors are involved. Having a systematic approach in place helps researchers stay organized and focused, leading to more accurate and impactful results.

When it comes to the scientific method, the first step is making observations. This involves using your senses to gather information about the world around you. It could be something as simple as noticing that plants in your garden are wilting, or as complex as observing the behavior of subatomic particles in a physics experiment. The key is to be curious and attentive to detail, as even the smallest observation could lead to a breakthrough in understanding.
One way to make observations is through quantitative data, which involves measuring and counting specific aspects of the phenomenon you’re studying. For example, a biologist may count the number of bird species in a particular area, or a chemist may measure the temperature at which a liquid boils. Qualitative data, on the other hand, focuses on the qualities or characteristics of the phenomenon. This could involve describing the color and texture of a rock, or the behavior of a particular animal.
By making observations at the beginning of the scientific method, you lay the groundwork for forming a hypothesis and designing experiments. It’s important to be thorough and objective in your observations, as bias or oversight could lead to inaccurate conclusions. With a keen eye and an open mind, the first step of the scientific method sets the stage for the journey of discovery and understanding.

Once you have made your observations, the next step in the scientific method is formulating a hypothesis. A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. It is an educated guess that is based on your observations and existing knowledge. In this step, you will use the information you gathered during the observation stage to come up with a statement that can be tested through experimentation.
It is important to note that a hypothesis is not just a random guess. It should be based on existing knowledge and should be testable. A good hypothesis is one that can be proven true or false through experimentation, and it should be clearly stated so that others can understand and test it as well.
When formulating a hypothesis, it is important to keep it simple and specific. Avoid making a vague or overly complicated statement, as this can make it difficult to test and evaluate. Additionally, make sure that your hypothesis is based on your observations and any relevant background information.
| Do | Don’t |
|---|---|
| Base your hypothesis on observations and existing knowledge | Make a vague or overly complicated statement |
| Keep your hypothesis simple and specific | Formulate a hypothesis that cannot be tested through experimentation |
By formulating a hypothesis, you are setting the stage for the next step in the scientific method, which is designing and conducting experiments to test your hypothesis.
Once you have formulated a hypothesis, the next crucial step in the scientific method is designing and conducting experiments. This step involves careful planning and execution to test the validity of your hypothesis. It is important to create a controlled environment in which to conduct your experiments, ensuring that only the variables you are interested in are being tested.
One way to design experiments is to create a detailed protocol outlining the steps necessary to carry out the experiment. This will help ensure that the experiment is conducted in a systematic and replicable manner. Additionally, it is important to consider ethical guidelines when designing and conducting experiments, especially when working with human or animal subjects.
Once the experiment has been designed, it is time to conduct the experiment according to the protocol you have created. This involves carefully following the steps outlined in the protocol and recording the results of the experiment. It is important to be thorough and precise in your observations and data collection to ensure the validity and reliability of your experiment.
In conclusion, the third step of the scientific method involves designing and conducting experiments to test the hypothesis formulated in the previous step. This step requires careful planning, attention to detail, and adherence to ethical guidelines to ensure the validity and reliability of the experimental results.

Once you have conducted your experiments and gathered the necessary data, the next crucial step in the scientific method is collecting and analyzing data. This step involves organizing and examining the information you have acquired through your experiments in order to draw meaningful conclusions.
During the data collection process, it is important to ensure that the information is accurate and consistent. This may involve recording measurements, observations, and any other relevant data in a systematic and organized manner. It is essential to maintain detailed records that can be used for later analysis and verification.
In addition to collecting data, it is equally important to analyze the information in a thorough and methodical manner. This may involve using statistical methods, graphs, charts, and other tools to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By carefully examining the information, scientists can gain valuable insights that can be used to support or refute their hypotheses.
Ultimately, the process of collecting and analyzing data is essential for drawing meaningful conclusions and advancing scientific knowledge. By carefully documenting and scrutinizing the information gathered from experiments, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and contribute to the body of knowledge within their respective fields.

What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a systematic way of learning about the world around us, involving observation, hypothesis formation, experimentation, and result interpretation.
What are the steps of the scientific method?
The steps of the scientific method include making observations, asking a question, forming a hypothesis, conducting experiments, analyzing the data, and drawing a conclusion.
Why is the scientific method important?
The scientific method is important because it helps ensure that scientific studies and experiments are conducted in a logical and objective manner, leading to reliable results.
Can the scientific method be applied outside of a laboratory setting?
Yes, the scientific method can be applied to everyday situations, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and understanding cause-and-effect relationships.
How does the scientific method promote critical thinking?
The scientific method promotes critical thinking by requiring evidence-based reasoning and logical evaluation of results, leading to a better understanding of the world and how it works.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon, while a theory is a well-substantiated explanation for a wide range of phenomena based on extensive evidence.
Are there any limitations to the scientific method?
Yes, some limitations of the scientific method include the inability to study certain phenomena, ethical considerations, and the possibility of human error in experimentation.