Breaking News


Popular News

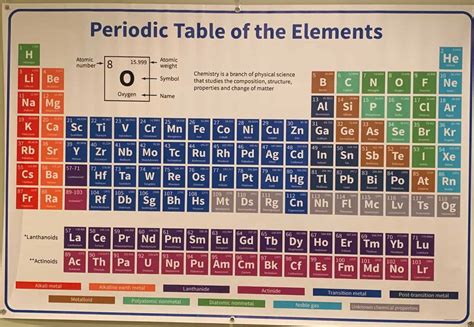
Discover the secrets of the periodic table, from its organization and properties to atomic structure and applications in chemistry.The periodic table of elements is a fundamental tool in the field of chemistry, serving as a comprehensive guide to the building blocks of matter. Understanding its intricacies is crucial for anyone looking to delve into the world of chemistry, whether as a student, researcher, or simply an enthusiast. In this blog post, we will unlock the mysteries of the periodic table, starting with an introduction to its basic principles. We will then explore the organization of elements within the table and delve into the properties that make each element unique. Additionally, we will discuss the fundamental concept of atomic structure and how it relates to the arrangement of elements in the table. Furthermore, we will examine the trends and patterns that emerge within the table, shedding light on the underlying principles of chemistry. Finally, we will explore the various applications of the periodic table in the field of chemistry, highlighting its crucial role in advancing scientific knowledge and technological innovations. Join us as we embark on a journey to uncover the secrets of the periodic table of elements.
Contents
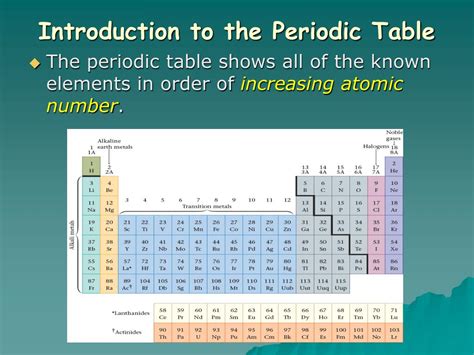
The Periodic Table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized in order of increasing atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. It was devised by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, who developed the periodic table to illustrate recurring trends in the properties of the elements. The table has proven to be an incredibly useful tool for chemists, students, and scientists in understanding the properties and behaviors of various chemical elements.
In addition, the Periodic Table consists of 118 confirmed elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and gold, which are arranged in groups and periods based on their atomic number. The table is further divided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, each with distinct properties and characteristics. The structure of the periodic table allows for the easy identification of elements and aids in the prediction of their chemical behavior.
Furthermore, the Periodic Table is essential for understanding the physical and chemical properties of the elements, as well as for predicting their behavior in chemical reactions. By organizing the elements in a systematic manner, the periodic table enables scientists to identify trends in properties such as atomic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity, and chemical reactivity. This information is crucial for the study and application of chemistry in various fields, from pharmaceuticals to materials science.
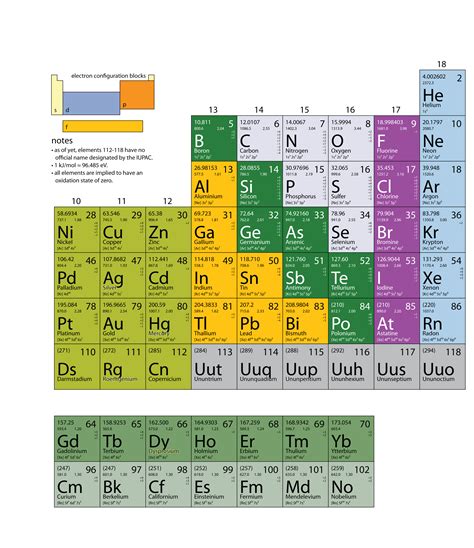
The organization of elements in the periodic table is based on their atomic number, which is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Each element is arranged in order of increasing atomic number from left to right and top to bottom. The periodic table is divided into groups and periods, with groups being the vertical columns and periods being the horizontal rows. It is also divided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, with the majority of elements being metals. The organization of elements in the table allows for easy identification of their properties and helps in understanding their behavior and relationships.
In addition to the arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, the periodic table also showcases various trends and patterns that exist within the elements. Elements within the same group often share similar chemical properties, while those in the same period exhibit similar physical properties. This organization helps in predicting the properties of unknown elements by comparing them to others within the same group or period.
Furthermore, the periodic table provides a systematic way to categorize and classify elements based on their characteristics. Elements are grouped together based on their electron configuration, which in turn determines their chemical reactivity and bonding behavior. This organization allows chemists to predict the behavior of elements in different chemical reactions, as well as their physical and chemical properties.
Overall, the organization of elements in the periodic table provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the properties and behaviors of the elements. It allows for the visualization of trends and patterns, which are essential for predicting the properties of unknown elements and for understanding the relationships between different elements. The periodic table’s organization plays a crucial role in the study of chemistry and is fundamental to the development of the field.
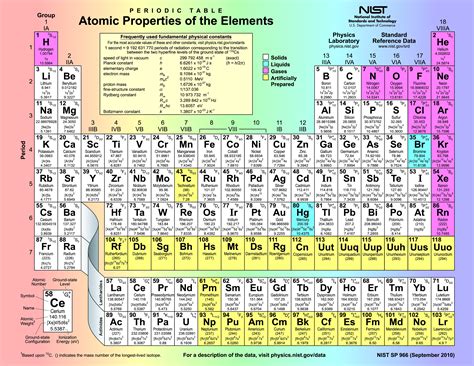
The properties of the elements in the periodic table are what make each one unique and important in the study of chemistry. These properties can be physical, such as melting and boiling points, or chemical, such as reactivity and ability to form bonds with other elements. Each element’s properties are determined by its atomic structure, including the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons it possesses. Understanding these properties is crucial for predicting how elements will interact with each other in different chemical reactions.
One way to organize and compare the properties of the elements is through the use of a table. The periodic table, first developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, organizes the elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. This organization allows scientists to easily identify trends and patterns in the properties of the elements, leading to a better understanding of their behavior.
One notable property of the elements is their ability to form compounds with each other. Some elements are highly reactive and readily form compounds with other elements, while others are inert and do not easily react with other substances. This ability to form compounds is essential for the diversity and complexity of the materials found in the natural world, as well as in the development of new substances in chemistry and industry.
Another important property of the elements is their physical state at standard temperature and pressure. The periodic table allows us to easily distinguish between elements that are gases, liquids, and solids. This information is crucial for understanding the behavior of these elements in different environments and is essential for many practical applications in chemistry and physics.
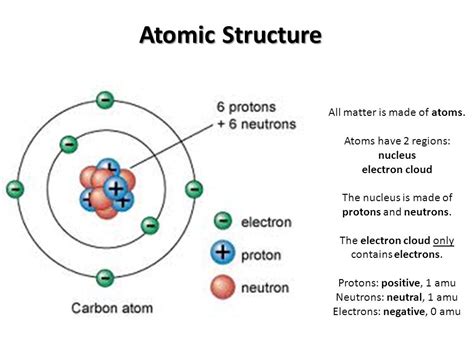
The atomic structure of an element is the foundation of the Periodic Table as it is based on the organization of atoms and their properties. Atoms are made up of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in energy levels. These subatomic particles play a crucial role in determining the chemical behavior of elements and their placement in the Periodic Table.
In the nucleus, protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge. The number of protons in the nucleus defines the atomic number of an element, which in turn determines its position in the Periodic Table. The arrangement of electrons in energy levels contributes to the chemical reactivity and bonding properties of the elements, leading to the formation of various compounds and molecules.
Understanding the atomic structure allows scientists to predict the behavior of elements, their physical properties such as melting and boiling points, and their chemical properties including reactivity and acidity. This knowledge forms the basis for the study of chemistry and the development of materials with specific properties for various applications in industries such as technology, medicine, and engineering.
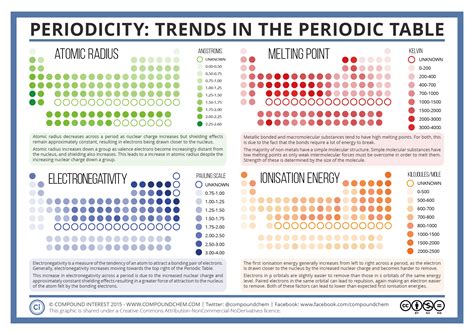
When we look at the periodic table of elements, we can observe various trends and patterns among the elements that are organized within it. These trends provide valuable insights into the behavior and properties of the elements, allowing scientists to make predictions and understand the relationships between different elements.
One of the most notable trends in the periodic table is the periodic law, which states that the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, with similar properties occurring at regular intervals. This law forms the basis for the organization of elements in the table and allows for the identification of trends related to atomic structure, chemical reactivity, and physical properties.
Another important pattern within the periodic table is the classification of elements into different groups and periods. Elements within the same group often share similar chemical properties, while elements within the same period exhibit trends in atomic size, ionization energy, and electronegativity. This organization helps scientists understand the systematic variations in properties as they move across a period or down a group.
Additionally, the periodic table highlights the concept of chemical periodicity, which refers to the recurring patterns of element properties across the table. Whether it’s the trend of increasing atomic radius down a group, or the trend of decreasing ionization energy across a period, these patterns provide a framework for understanding the behavior of elements in relation to their position in the table.
The Periodic Table of Elements is an incredibly useful tool for chemists, as it provides a systematic way to organize and categorize the known elements. One of the main applications of the periodic table in chemistry is predicting the behavior of elements and their compounds. By using the table, chemists can determine the physical and chemical properties of elements based on their position in the table.
Another important application of the periodic table in chemistry is in understanding the reactivity of elements. The table allows chemists to predict the reactivity of elements and their likelihood to form compounds with other elements. This is crucial in chemical reactions and in the development of new materials and compounds.
Furthermore, the periodic table is used in the field of analytical chemistry for identifying and characterizing unknown substances. By comparing the properties of an unknown substance with those of known elements, chemists can determine the composition and structure of the substance, aiding in the process of chemical analysis.
In addition, the periodic table is indispensable in the study of periodic trends and patterns, such as electronegativity, ionization energy, and atomic radius. These trends provide valuable insights into the behavior of elements and their compounds, and are fundamental to our understanding of chemical principles.

What is the Periodic Table of Elements?
The Periodic Table of Elements is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
How many elements are there in the Periodic Table?
There are currently 118 confirmed elements in the Periodic Table.
Who created the first version of the Periodic Table?
The first version of the Periodic Table was created by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869.
What are some common properties of the elements in the same group in the Periodic Table?
Elements in the same group in the Periodic Table often share similar chemical properties and react in similar ways.
What are the periods in the Periodic Table?
The periods in the Periodic Table refer to the rows, with elements in the same period having the same number of atomic orbitals.
Why are some elements in the Periodic Table shown in parentheses?
Some elements are shown in parentheses in the Periodic Table to indicate that they are synthetic or have a very short half-life.
What is the significance of the noble gases in the Periodic Table?
The noble gases are significant for their stability and lack of reactivity, making them valuable in various industrial and scientific applications.