Breaking News


Popular News

Discover the reasons behind eclipses and their significance. Learn about different types, solar and lunar eclipse processes, and influencing factors. Have you ever gazed up at the sky and witnessed the mesmerizing phenomenon of an eclipse? Eclipses have captivated humans for centuries, leaving us in awe of the celestial dance between the sun, moon, and earth. In this blog post, we will explore the intriguing world of eclipses, delving into their different types, the fascinating processes behind solar and lunar eclipses, and the factors that contribute to their occurrence. We will also uncover the significance of eclipses and why they hold a special place in the hearts of astronomers, astrologers, and sky watchers alike. So, join us as we unravel the mysteries of eclipses and discover the magic that unfolds when the sun, moon, and earth align in perfect harmony.
Contents

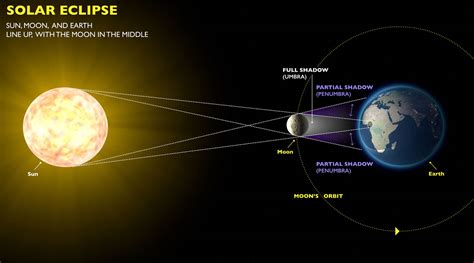
Eclipses are astronomical events that occur when one celestial body passes in front of another, causing a temporary shadow to be cast. This can happen between the Earth, the Sun, and the Moon. When the Moon comes between the Earth and the Sun, a solar eclipse occurs. Conversely, when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, a lunar eclipse occurs. These events can be partial, total, or annular, depending on the alignment of the bodies involved.
During a solar eclipse, the Moon blocks the light from the Sun, casting a shadow on certain areas of the Earth and creating the illusion of a darkened daytime sky. This phenomenon has been the subject of fascination and fear throughout history, with many cultures developing myths and legends to explain these celestial events. On the other hand, a lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth’s shadow falls on the Moon, giving it a reddish hue and making it appear larger in the sky.
These eclipses occur due to the orbit and alignment of the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun. While these events may seem mystical or supernatural, they can be scientifically predicted and explained, adding to our understanding of the astronomical world around us.
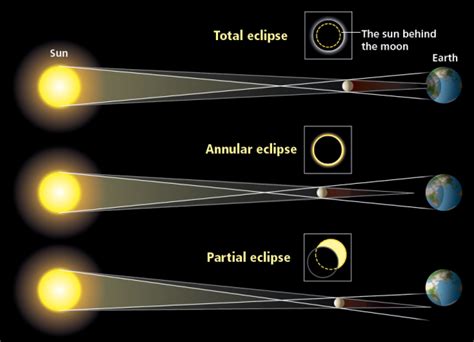
There are two main types of eclipses: solar eclipses and lunar eclipses. Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes between the Earth and the Sun, blocking the Sun’s light and casting a shadow on the Earth. This can result in a partial or total solar eclipse, depending on the viewer’s location within the path of totality. Lunar eclipses, on the other hand, occur when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon, causing the Earth’s shadow to fall on the Moon. This can create a partial or total lunar eclipse, depending on the alignment of the three celestial bodies.
Within these two main types, there are further subcategories. For solar eclipses, there are three types: total, partial, and annular. In a total solar eclipse, the Moon completely covers the Sun, creating a brief period of darkness known as totality. In a partial solar eclipse, the Moon only partially covers the Sun, creating a crescent shape of sunlight. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon is too far from the Earth to completely cover the Sun, resulting in a ring of sunlight around the edges of the Moon.
For lunar eclipses, the subcategories are penumbral, partial, and total. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth’s penumbral shadow, creating a subtle darkening of the lunar surface. A partial lunar eclipse happens when only a portion of the Moon enters the Earth’s umbral shadow, causing a section of the Moon to darken. A total lunar eclipse occurs when the entire Moon enters the Earth’s umbral shadow, resulting in a dramatic reddish hue known as a blood moon.
In conclusion, the various types of eclipses offer unique astronomical phenomena that captivate viewers and provide a deeper understanding of the celestial mechanics at play. Whether witnessing the fleeting beauty of a total solar eclipse or the ethereal glow of a blood moon, each type of eclipse offers a mesmerizing experience for enthusiasts of astronomy and natural wonders.

The Solar Eclipse Phenomenon
Eclipses are one of the most intriguing natural phenomena that occur in our solar system. A solar eclipse happens when the moon passes between the sun and the Earth, blocking all or a portion of the sun’s light. This phenomenon occurs only during a new moon when the sun, moon, and Earth are aligned in a straight line.
There are three main types of solar eclipses: total, partial, and annular. During a total solar eclipse, the moon completely covers the sun, darkening the sky and revealing the sun’s outer atmosphere, known as the solar corona. In a partial solar eclipse, only a part of the sun is obscured by the moon, resulting in a crescent-shaped sun. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the moon is at its farthest point from Earth, causing it to appear smaller and block most of the sun’s light, leaving a bright ring, or annulus, around the edges.
The duration and visibility of a solar eclipse depend on various factors, such as the moon’s distance from Earth, the tilt of the moon’s orbit, and the Earth’s axial tilt. Total solar eclipses are considered rare events and are only visible along a narrow path on Earth’s surface. People within the path of totality can experience the awe-inspiring sight of the sun being completely obscured by the moon, plunging the surroundings into darkness in the middle of the day.
The solar eclipse phenomenon has captivated and inspired people throughout history, leading to the development of myths, superstitions, and scientific discoveries. From ancient civilizations to modern astronomers, the significance of solar eclipses continues to intrigue and fascinate individuals around the world.
| Type of Eclipse | Description |
|---|---|
| Total Solar Eclipse | The moon completely covers the sun, revealing the solar corona. |
| Partial Solar Eclipse | Only a part of the sun is obscured by the moon, resulting in a crescent-shaped sun. |
| Annular Solar Eclipse | The moon appears smaller, leaving a bright ring around the edges of the sun. |
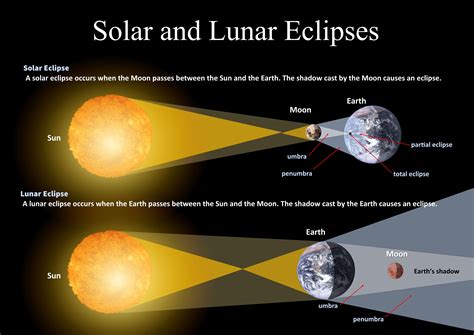
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Earth passes between the Moon and the Sun, casting a shadow on the Moon. There are three types of lunar eclipses: total, partial, and penumbral.
In a total lunar eclipse, the Earth completely blocks the Sun’s light from reaching the Moon, causing the entire Moon to be in shadow. During a partial lunar eclipse, only a portion of the Moon is covered by the Earth’s shadow. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes through the Earth’s penumbral shadow, resulting in a subtle darkening of the Moon.
These eclipses can only occur during a full moon when the Moon is directly opposite the Sun in the sky. The alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun must be almost perfect for a lunar eclipse to take place, which is why they are relatively rare events.
During a lunar eclipse, the Moon can appear to take on different colors, such as red or orange, due to the Earth’s atmosphere

Factors Influencing Eclipses
Eclipses occur when the Sun, Moon, and Earth align in a specific way, creating shadows and blocking light from reaching certain areas. There are several factors that influence the occurrence of eclipses, including the tilt of the Earth’s axis, the distance between the Sun, Moon, and Earth, and the orbital paths of these celestial bodies.
Firstly, the tilt of the Earth’s axis plays a crucial role in the occurrence of eclipses. This tilt causes the alignment of the Sun, Moon, and Earth to vary, which in turn affects the frequency and type of eclipses that occur. When the alignment is just right, a solar or lunar eclipse can take place, creating a stunning astronomical event.
Furthermore, the distance between the Sun, Moon, and Earth also impacts the occurrence of eclipses. The distance between these celestial bodies can affect the size and duration of an eclipse, as well as its visibility from different regions of the Earth. A closer alignment can result in a total eclipse, while a farther alignment may cause a partial eclipse to occur.
In addition, the orbital paths of the Sun, Moon, and Earth affect the frequency and timing of eclipses. These orbital paths determine when and where eclipses can be observed, as well as how often they occur. Understanding these paths is essential for predicting and studying eclipses, providing valuable insights into the movements and interactions of celestial bodies.

There are various significances attached to eclipses in different cultures around the world. In many ancient civilizations, eclipses were considered as harbingers of significant events or warnings from the gods. The occurrence of an eclipse was often associated with fear, superstitions, and religious rituals, as people believed that the alignment of the sun, moon, and earth had a powerful impact on human life.
Furthermore, eclipses have played a crucial role in scientific discoveries and advancements. For instance, during a solar eclipse in 1919, scientists were able to prove Einstein’s theory of general relativity, which revolutionized our understanding of the universe. The study of eclipses has also led to significant discoveries in the fields of astronomy, physics, and space exploration, providing valuable insights into the mechanics of our solar system and beyond.
Moreover, eclipses have a symbolic significance in many cultures, representing themes of transformation, renewal, and change. The temporary darkening of the sun or moon during an eclipse is often interpreted as a metaphor for introspection, inner growth, and the cyclical nature of existence. In astrology, eclipses are believed to have profound effects on individual and collective consciousness, influencing personal growth, relationships, and societal dynamics.
In conclusion, the significance of eclipses extends beyond their celestial spectacle, encompassing cultural, scientific, and symbolic dimensions. Whether viewed as omens, scientific phenomena, or cosmic symbols, eclipses continue to captivate the human imagination and inspire awe and wonder across the globe.
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the earth, blocking all or part of the sun’s rays from reaching the earth.
What causes a lunar eclipse?
A lunar eclipse occurs when the earth passes between the sun and the moon, causing the earth’s shadow to fall on the moon.
How often do eclipses happen?
Eclipses do not occur every month because the moon’s orbit is tilted relative to the earth’s orbit around the sun.
Why are some eclipses total while others are partial?
The type of eclipse (total or partial) depends on the alignment of the sun, moon, and earth, and the distance between them during the eclipse.
Are eclipses dangerous to observe?
It is not safe to look at a solar eclipse directly without proper protection, but lunar eclipses are safe to view with the naked eye.
Can eclipses be predicted in advance?
Yes, eclipses can be predicted years in advance using mathematical models and precise measurements of the orbits of the sun, moon, and earth.
Do eclipses have any cultural or historical significance?
Many ancient cultures and civilizations viewed eclipses as omens or supernatural events, and they often played a role in religious or mythological beliefs.